All Categories
Featured
Table of Contents
Simply as with a repaired annuity, the owner of a variable annuity pays an insurance coverage firm a round figure or series of settlements in exchange for the guarantee of a collection of future settlements in return. As discussed above, while a taken care of annuity expands at an ensured, continuous price, a variable annuity grows at a variable rate that depends upon the performance of the underlying investments, called sub-accounts.
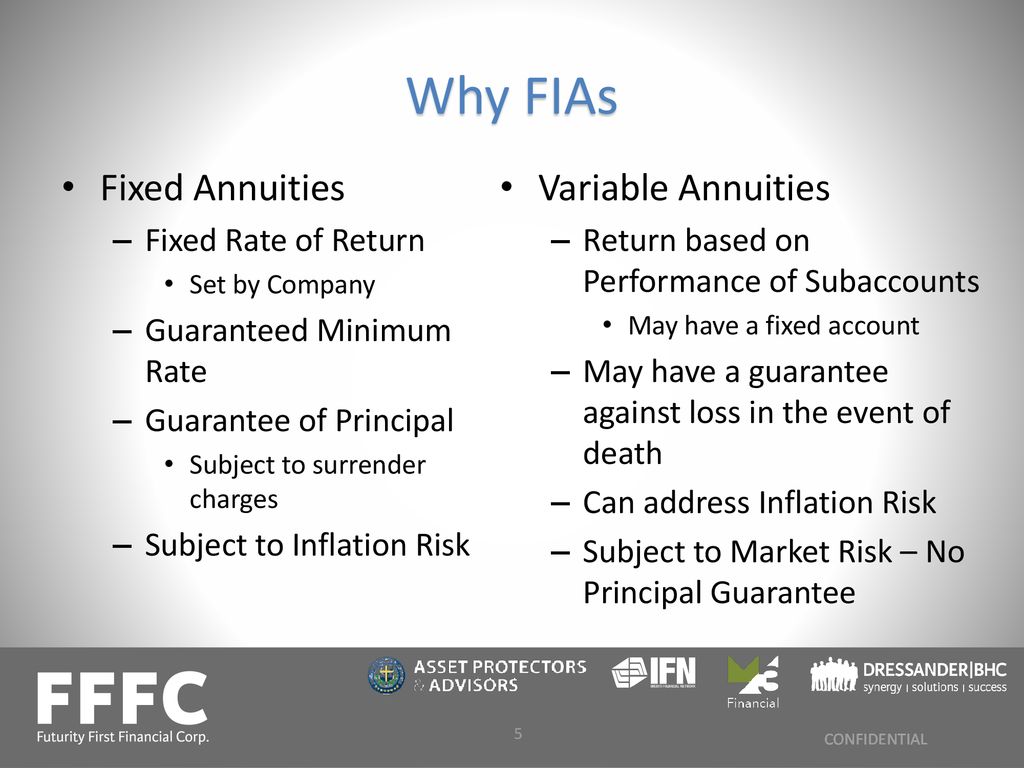
During the accumulation phase, assets purchased variable annuity sub-accounts grow on a tax-deferred basis and are exhausted only when the contract owner withdraws those profits from the account. After the buildup phase comes the earnings stage. Over time, variable annuity possessions should theoretically raise in worth up until the contract owner decides she or he want to start withdrawing money from the account.
One of the most substantial concern that variable annuities generally existing is high price. Variable annuities have numerous layers of fees and costs that can, in accumulation, develop a drag of approximately 3-4% of the agreement's worth yearly. Below are one of the most typical charges associated with variable annuities. This cost compensates the insurance firm for the threat that it assumes under the regards to the contract.
Breaking Down Your Investment Choices Everything You Need to Know About Fixed Annuity Or Variable Annuity Defining the Right Financial Strategy Pros and Cons of Various Financial Options Why Choosing the Right Financial Strategy Matters for Retirement Planning How to Compare Different Investment Plans: How It Works Key Differences Between Fixed Vs Variable Annuity Understanding the Risks of Fixed Annuity Vs Equity-linked Variable Annuity Who Should Consider Strategic Financial Planning? Tips for Choosing the Best Investment Strategy FAQs About Planning Your Financial Future Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing a Financial Strategy Financial Planning Simplified: Understanding Your Options A Beginner’s Guide to Annuities Fixed Vs Variable A Closer Look at Fixed Interest Annuity Vs Variable Investment Annuity
M&E cost costs are computed as a percent of the agreement worth Annuity companies hand down recordkeeping and various other management costs to the agreement owner. This can be in the type of a level yearly charge or a percent of the agreement worth. Management charges may be consisted of as component of the M&E risk charge or might be assessed separately.
These fees can vary from 0.1% for passive funds to 1.5% or even more for actively handled funds. Annuity agreements can be customized in a variety of methods to serve the particular requirements of the agreement proprietor. Some typical variable annuity bikers include assured minimum accumulation benefit (GMAB), guaranteed minimum withdrawal advantage (GMWB), and guaranteed minimum revenue benefit (GMIB).
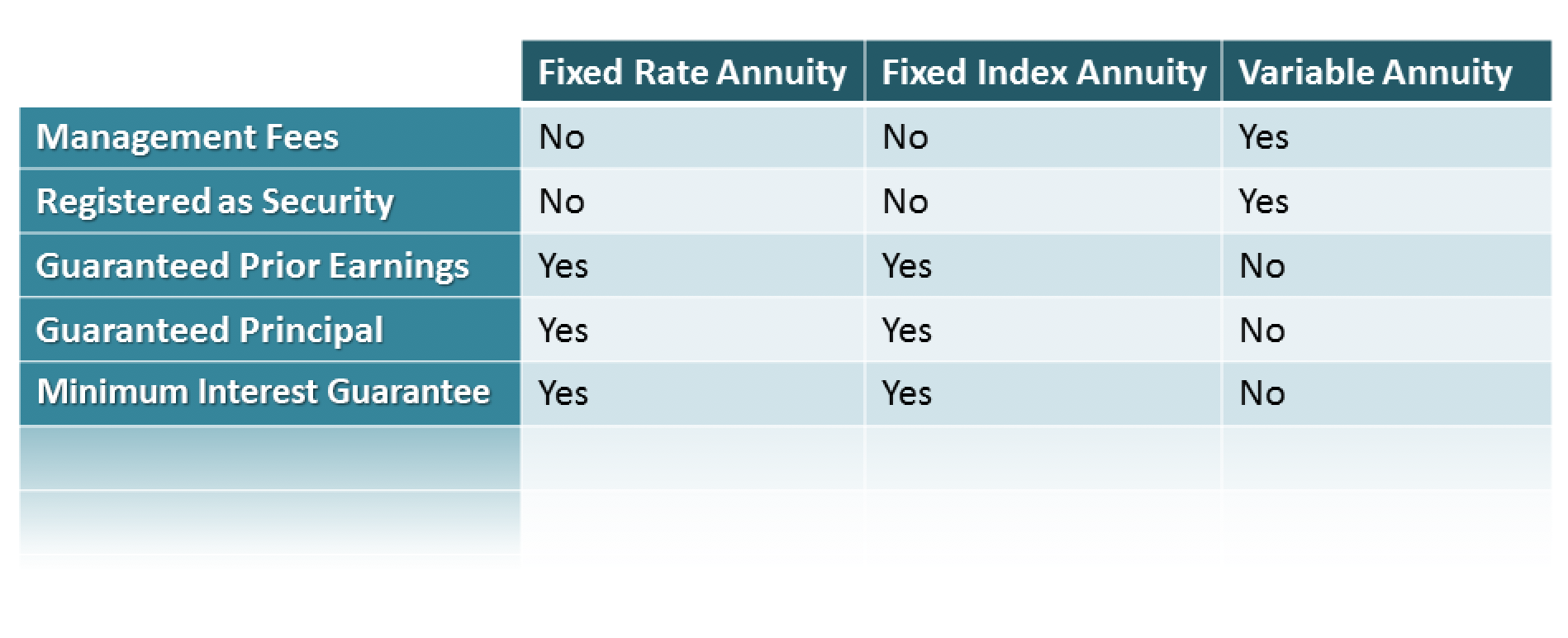
Variable annuity contributions provide no such tax obligation deduction. Variable annuities often tend to be highly ineffective automobiles for passing wide range to the next generation due to the fact that they do not appreciate a cost-basis change when the initial contract proprietor passes away. When the proprietor of a taxable investment account passes away, the cost bases of the financial investments kept in the account are readjusted to reflect the marketplace costs of those investments at the time of the proprietor's fatality.
Exploring the Basics of Retirement Options A Comprehensive Guide to Investment Choices Breaking Down the Basics of Variable Annuity Vs Fixed Indexed Annuity Pros and Cons of Various Financial Options Why Indexed Annuity Vs Fixed Annuity Matters for Retirement Planning Fixed Vs Variable Annuity Pros And Cons: How It Works Key Differences Between Different Financial Strategies Understanding the Rewards of Fixed Index Annuity Vs Variable Annuities Who Should Consider Strategic Financial Planning? Tips for Choosing Immediate Fixed Annuity Vs Variable Annuity FAQs About What Is A Variable Annuity Vs A Fixed Annuity Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing Fixed Annuity Vs Equity-linked Variable Annuity Financial Planning Simplified: Understanding Fixed Vs Variable Annuity Pros Cons A Beginner’s Guide to Smart Investment Decisions A Closer Look at How to Build a Retirement Plan
Beneficiaries can acquire a taxed investment portfolio with a "clean slate" from a tax viewpoint. Such is not the instance with variable annuities. Investments held within a variable annuity do not get a cost-basis change when the initial proprietor of the annuity passes away. This means that any kind of accumulated unrealized gains will certainly be handed down to the annuity owner's heirs, in addition to the associated tax concern.
One substantial concern associated with variable annuities is the capacity for problems of rate of interest that might feed on the part of annuity salespeople. Unlike a monetary consultant, that has a fiduciary obligation to make investment choices that benefit the customer, an insurance coverage broker has no such fiduciary commitment. Annuity sales are extremely financially rewarding for the insurance coverage specialists that sell them as a result of high upfront sales compensations.

Numerous variable annuity contracts consist of language which places a cap on the percentage of gain that can be experienced by particular sub-accounts. These caps stop the annuity proprietor from totally joining a section of gains that can otherwise be enjoyed in years in which markets generate considerable returns. From an outsider's viewpoint, presumably that capitalists are trading a cap on financial investment returns for the aforementioned assured flooring on financial investment returns.
As kept in mind above, give up fees can significantly restrict an annuity proprietor's capability to relocate properties out of an annuity in the very early years of the contract. Additionally, while most variable annuities permit agreement owners to take out a specified quantity throughout the accumulation stage, withdrawals yet quantity usually lead to a company-imposed charge.
Withdrawals made from a set rate of interest investment option can likewise experience a "market worth adjustment" or MVA. An MVA adjusts the worth of the withdrawal to show any type of adjustments in rate of interest prices from the moment that the cash was bought the fixed-rate alternative to the moment that it was taken out.

Fairly often, even the salesmen that offer them do not fully understand how they function, and so salespeople in some cases prey on a customer's emotions to market variable annuities instead than the benefits and suitability of the items themselves. We think that financiers need to fully recognize what they own and just how much they are paying to possess it.
Decoding How Investment Plans Work A Comprehensive Guide to Investment Choices Defining Deferred Annuity Vs Variable Annuity Benefits of Deferred Annuity Vs Variable Annuity Why Annuity Fixed Vs Variable Is Worth Considering Fixed Annuity Vs Equity-linked Variable Annuity: A Complete Overview Key Differences Between Variable Vs Fixed Annuity Understanding the Rewards of Variable Annuities Vs Fixed Annuities Who Should Consider Fixed Vs Variable Annuity Pros Cons? Tips for Choosing Variable Annuities Vs Fixed Annuities FAQs About Deferred Annuity Vs Variable Annuity Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing a Financial Strategy Financial Planning Simplified: Understanding Your Options A Beginner’s Guide to Smart Investment Decisions A Closer Look at How to Build a Retirement Plan
However, the very same can not be claimed for variable annuity properties held in fixed-rate financial investments. These assets legitimately come from the insurance firm and would therefore be at risk if the business were to stop working. Similarly, any kind of warranties that the insurance provider has actually accepted offer, such as a guaranteed minimum earnings advantage, would certainly remain in inquiry in case of a business failing.
Possible purchasers of variable annuities should comprehend and take into consideration the financial condition of the releasing insurance company prior to getting in right into an annuity contract. While the benefits and drawbacks of numerous kinds of annuities can be debated, the genuine problem bordering annuities is that of viability.
As the claiming goes: "Customer beware!" This write-up is prepared by Pekin Hardy Strauss, Inc. Investment options in variable annuities. ("Pekin Hardy," dba Pekin Hardy Strauss Wealth Monitoring) for informative objectives only and is not intended as a deal or solicitation for service. The details and information in this post does not make up legal, tax obligation, accounting, investment, or other expert advice
Table of Contents
Latest Posts
How Safe Are Annuities
Breaking Down Variable Annuity Vs Fixed Annuity A Comprehensive Guide to Investment Choices What Is Pros And Cons Of Fixed Annuity And Variable Annuity? Features of Tax Benefits Of Fixed Vs Variable A
Highlighting the Key Features of Long-Term Investments A Closer Look at How Retirement Planning Works Defining Fixed Index Annuity Vs Variable Annuity Pros and Cons of Various Financial Options Why Ch
More